Advances in research on the autism spectrum

Dora Raymaker (left) and Christina Nicolaidis by BEN JACKLET
Recent advances in autism spectrum disorder (ASD) research have significantly expanded our understanding of this complex neurodevelopmental condition.
These insights span multiple areas, including genetics, neurobiology, and innovative therapeutic approaches.
Genetic Insights
The genetic architecture of ASD is increasingly recognized as highly complex.
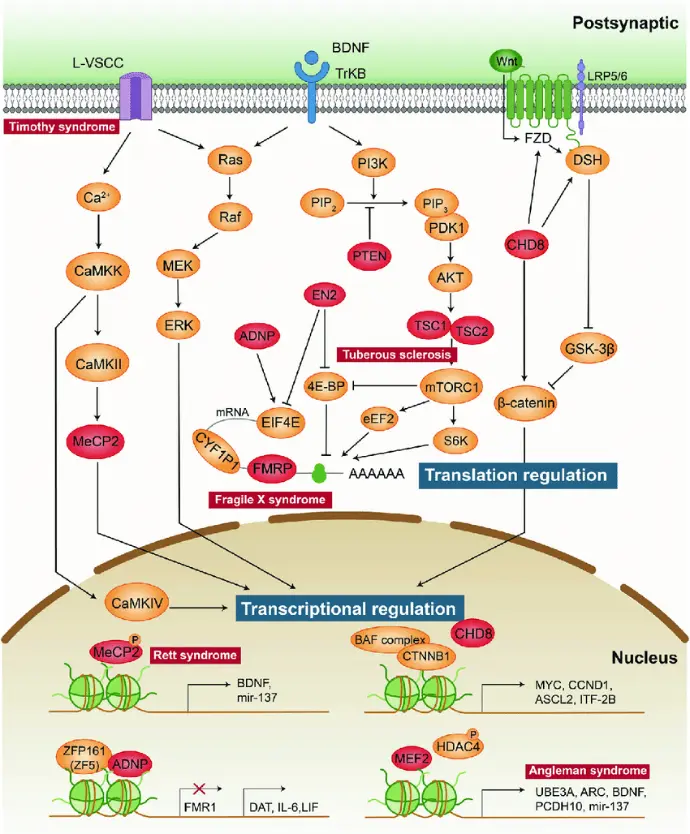
Signalling pathways in autism spectrum disorder: mechanisms and therapeutic implications - Scientific Figure on ResearchGate. [accessed 2 Dec 2024]
Recent genomic technologies have revealed a intricate interplay of factors contributing to ASD risk:
- Common and rare genetic variants
- De novo mutations
- Epigenetic factors
These genetic findings have implicated key biological pathways, brain regions, and cell types in ASD pathophysiology.
In the Chinese population, structural variations (SVs) have been identified as potentially significant contributors to ASD risk, highlighting the importance of studying diverse ethnic groups to fully understand the genetic landscape of ASD.
Neurobiological Alterations
Neuroanatomical and neurobiological changes associated with ASD have been a focus of recent research:
- Neurobehavioral deficits impacting daily living activities
- Both genetic and non-genetic factors contribute to ASD etiopathogenesis
- Diverse and complex mechanisms underlie ASD pathology
Understanding these neurobiological alterations is crucial for developing effective therapies and potential biomarkers for early detection and intervention.
Hormonal Biomarkers
An intelligent framework using fuzzy logic has been developed to predict ASD severity based on hormonal biomarkers.
This approach focuses on four key hormones:
- Serotonin
- Oxytocin
- Melatonin
- Vitamin D
Findings suggest that high levels of Serotonin and very low levels of Vitamin D and Melatonin significantly influence ASD severity.
This novel approach offers promise for early diagnosis and intervention strategies.
Robot-Assisted Cognitive Training (RACT)
ZENO - A Robot by Robts4Autism | Picture from: Autism360

An Innovative Therapeutic Approaching
Robot-Assisted Cognitive Training for Children with Autism Insights and Outcomes Research has explored the potential benefits of RACT for children with ASD:
- Combines cognitive tasks with dynamic robotic technology
- Significant improvements in both quantitative and qualitative measures of cognitive ability
- Shows promise for enhancing cognitive functioning in children with ASD.
While initial results are encouraging, further research is needed to refine RACT processes and make them accessible to a broader range of children with ASD.
Adult-Specific Research
Most research and writing about autism is focused on children, although most autistic people are adults. - Daniel Smeenk
3,5%
But there has been an increasing focus on studying autism in adults, leading to a better understanding of adult outcomes, challenges, and support needs.
Autistica's research at Newcastle University aims to enhance the diagnosis and support for autistic adults by understanding their life experiences and health needs.
The research involves a national cohort, the Adult Autism Spectrum Cohort (AASC-UK), which collects data through surveys, interviews, and focus groups to identify health patterns and research preferences.
This approach helps develop personalized therapies, improve mental and physical health outcomes, and enhance the quality of life for autistic individuals.
Autistic adults have amazing skills when it comes to mental imagery
Recent studies have found that autistic adults may possess unique strengths in mental imagery, with some aspects being superior to non-autistic individuals.
Specifically, autistic individuals have shown enhanced abilities in visual memory and certain stages of mental imagery, such as maintaining visual patterns and inspecting mental images.
In tasks like the visual pattern test, autistic participants demonstrated a higher span, indicating better maintenance of mental images.
Additionally, they were equally fast in image scanning tasks regardless of distance, unlike non-autistic individuals whose response times varied with distance.
Autistic adults are in fact acutely aware of their feelings and can label them in vivid, often colorful detail.
A recent study by Rutgers University challenges the common perception that autistic adults struggle with emotional awareness.
Contrary to previous beliefs, many autistic adults are acutely aware of their emotions and can describe them in vivid, colorful detail.
The study involved focus groups with autistic adults aged 18 to 35, who used rich language to express their emotions, often combining traditional emotional words with physical sensations.
For example, emotions like giddiness might be described as "bees," while anger could feel like a "body-tensing" boil.
This finding suggests the need for therapy strategies that focus on mutual understanding rather than changing how autistic individuals communicate
The Silent Struggle: Suicide Risks in the Autism Community - What the Numbers Reveal
Recent research Global Burden of Disease Study 2021 paints a critical picture of mental health challenges within the autism community. Here's what we've learned:
• 3x Higher Risk: Studies show that individuals with autism are more than 3 times more likely to attempt suicide compared to the general population.
• Early Onset: These elevated risks start incredibly early - from as young as 10 years old, autistic individuals face significantly higher suicide rates.
• Consistent Across Ages: This isn't a problem confined to one age group. The increased risk remains consistent across different life stages.
These numbers aren't just statistics - they're a urgent call to understand, support, and protect our neurodivergent community members.
Why are these numbers so high? Factors include:
• Social isolation
• Communication challenges
• Difficulty expressing emotional pain
• Lack of understanding from society
• Limited mental health support
Remember: Every number represents a human life. With awareness, compassion, and proper support, we can make a difference.
In 2024, several prominent institutions and NGOs continue to provide crucial support for autistic individuals and their families worldwide.
Global Organizations

Autism Speaks: One of the world's largest autism advocacy organizations, Autism Speaks focuses on advancing research, increasing awareness, and providing support to individuals and families affected by autism.

World Autism Organisation: This global body works to promote the highest possible quality of life for people with autism and their families. They advocate for measures to improve life quality, develop and recommend best practices, and coordinate efforts of national member associations.

Global Autism Project: A US-based non-profit with over 20 years of experience, the Global Autism Project builds capacity for autism services worldwide. They partner with organizations globally to improve services and increase autism awareness at the local level.
Regional and National Organizations
United States:
- Autism Society of America (ASA): The nation's leading autism organization, founded in 1965.
- Autism Science Foundation (ASF): Provides funding for autism research and disseminates scientific findings.
- Autism Research Institute (ARI): Focuses on conducting and funding research to improve the lives of individuals with autism.
United Kingdom:
- National Autistic Society: A prominent UK-based charity working to improve the lives of autistic individuals and their families.
Europe:
- Autism-Europe: An international association that advocates for the rights of autistic people and their families.
Australia:
- Autism Spectrum Australia (Aspect): One of the largest autism-specific service providers in the country.
Research and Support Organizations
Association for Science in Autism Treatment: Promotes science-based interventions for individuals with autism.
Autism Network International (ANI): A uniquely autistic-run advocacy and self-help organization.
OASIS MAAP Services for Autism, Asperger Syndrome & PDD: Provides information and support for individuals with autism spectrum disorders.
Government Institutions
National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD): Conducts and supports research on autism and related conditions.
National Institute on Deafness & Other Communication Disorders Information Clearing House (NIDCD): Provides resources on communication disorders, including those associated with autism.
National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH): Supports and conducts research on mental health conditions, including autism.
These organizations collectively work towards improving understanding, acceptance, and support for autistic individuals globally. They offer various services ranging from research funding and advocacy to direct support and community building.
